Complex road environments, such as highway intersections and tile borders, demand highly accurate digital representations to ensure vehicles can navigate efficiently and safely. NDS.Live offers a standardized approach to modeling these complex intersections, enabling seamless integration across navigation systems, sensors, and mapping data.
By adopting NDS.Live standard, automotive and mapping companies can eliminate interoperability issues, reduce development costs, and foster innovation. This article explores best practices for modeling complex intersections on highways and tile borders using NDS.Live, ensuring accurate and reliable navigation in real-world scenarios.
In NDS.Live, an intersection lane group always covers the entire intersection, with its lanes directly connected to those from surrounding lane groups going in and out of the intersection. However, when a tile border cuts through an intersection, a different modeling approach is required to maintain connection between the lanes.
To address this, NDS.Live implements a solution where the complete intersection lane group remains within one tile. At the tile border, a border lane group is introduced to ensure smooth connectivity between the intersection lanes and the road lane groups in the adjacent tile. This approach ensures that the lane connections are maintained across tile borders, providing a seamless experience for navigation and mapping systems.
Practical example
Let’s take a complex intersection located at real GPS coordinates: 51.046176305682216, 13.754924734944355. To help visualize how NDS.Live models such intersections, we create a simplified representation. The figure outlines the intersection lane group, but keep in mind that this is just one possible way to structure it.
In a real-world project, the starting and ending points of the intersection lane group could vary depending on specific requirements and road configurations. This flexibility allows for accurate and adaptable modeling of intersections in diverse environments.
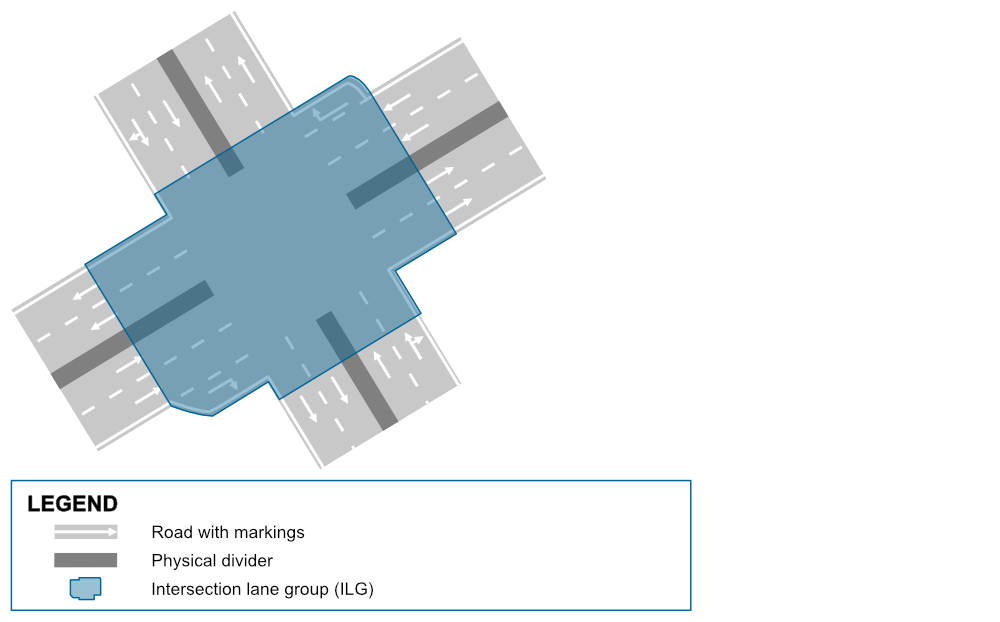
In a typical scenario, the lanes from the intersection lane group seamlessly connect to the lanes of the surrounding road lane groups that go in and out of the intersection. However, in this case, a tile border cuts through the intersection, meaning that four of the road lane groups—two to the east and two to the south—are stored in a different tile.
To manage this, NDS.Live ensures that the entire intersection lane group is logically stored in one tile, referred to as Tile A, even though part of the intersection physically resides in another tile, Tile B. This approach allows the system to maintain a consistent and accurate representation of the intersection across tile borders, ensuring smooth lane transitions and accurate navigation data.
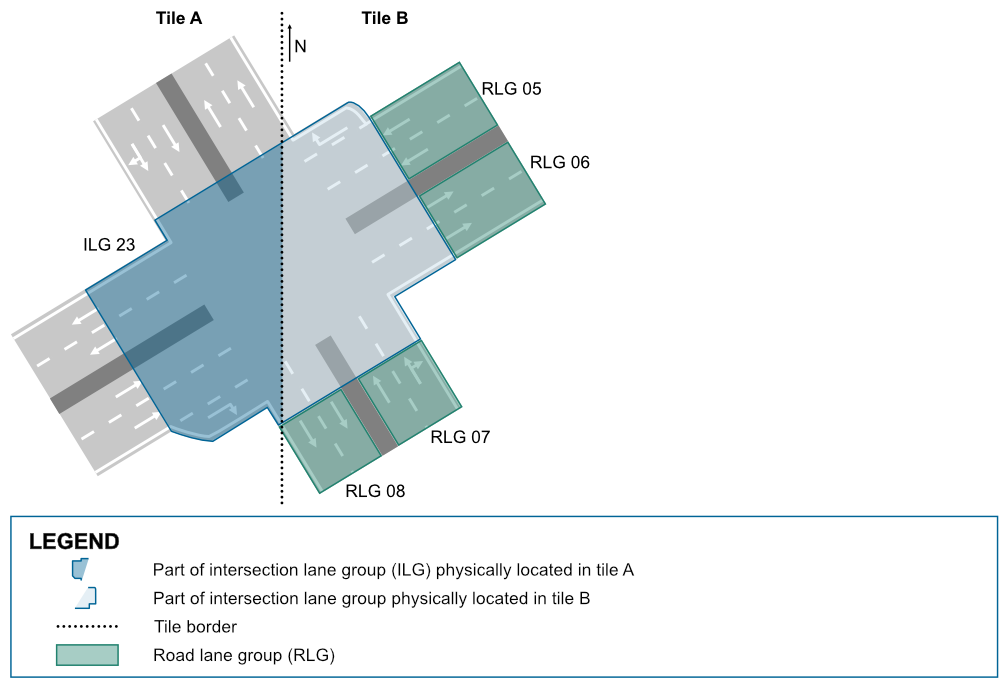
To ensure proper connectivity between the intersection lane group in Tile A and the road lane groups in Tile B, NDS.Live introduces two border lane groups at each side of the tile border. These border lane groups act as connectors, linking the lanes of the intersection to those in the adjacent tile.
In a simplified visualization, Tile A contains the intersection lane group, while Tile B holds the road lane groups. The connection between them is established through zero-length lanes in the four border lane groups.
The following diagram focuses on illustrating the logical connections between tiles disregarding geometric details, which is why the tile border appears as a 90° angle, even though it’s a straight line in reality. For clarity, lanes that don’t connect to the border lane groups are grayed out, and all lanes are shown in the direction of travel.
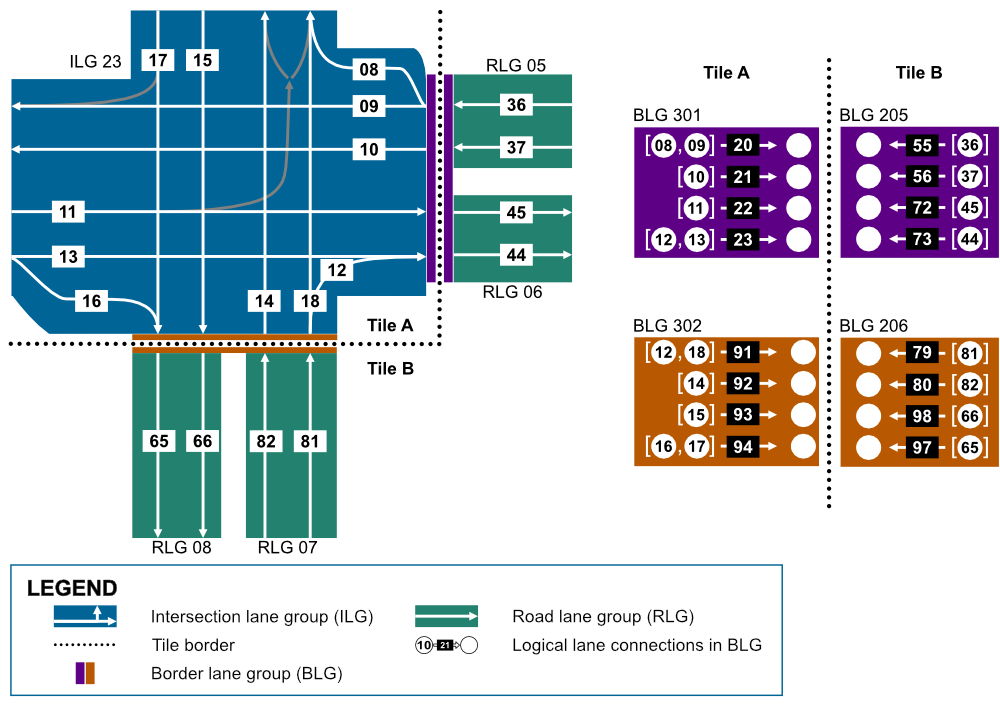
In such a way, NDS.Live simplifies modeling complex intersections on tile by using border lane groups to maintain lane connectivity across the tiles. This method ensures accurate, real-time navigation data, even in scenarios where road sections span multiple tiles.
In some countries, roads that are classified as motorways in NDS.Live feature complex intersections that lack physical dividers, such as guardrails, particularly in entry and exit scenarios. Complex intersections on highways require a unique approach to ensure safe and efficient navigation.
Let’s consider the example where GPS coordinates 40.28792638115781, 116.07647247784121 showcase a complex intersection involving both an entry and exit point. The figure below represents the simplified real-world intersection, highlighting how NDS.Live can effectively model such scenarios to ensure accuracy and safety.
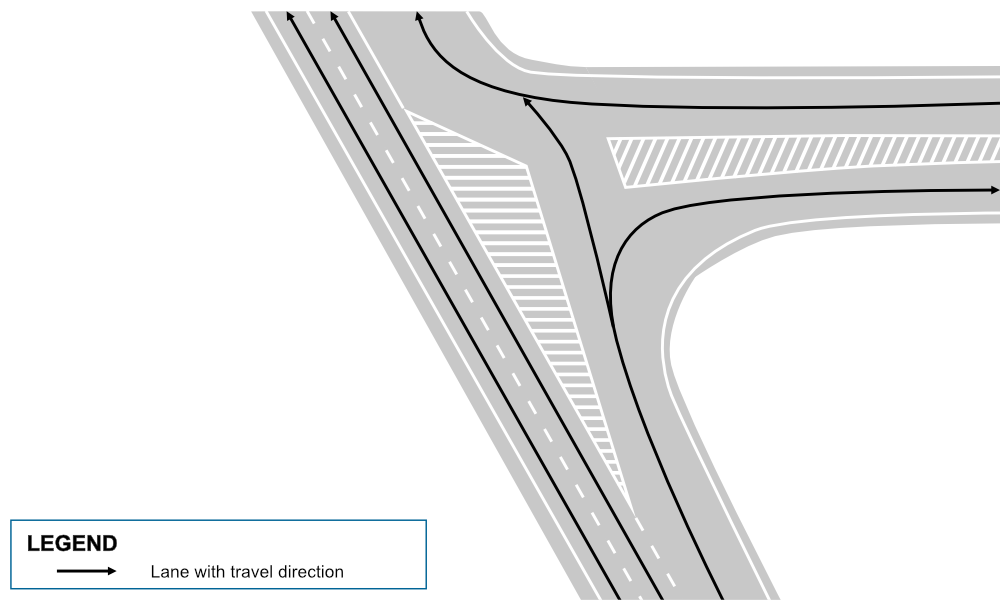
Example with functioning intersection lane group
For functional safety reasons, complex highway intersections like this must be modeled using an intersection lane group. This approach ensures that the lanes are organized correctly and safely in these complex road layouts, as demonstrated in the following figure.
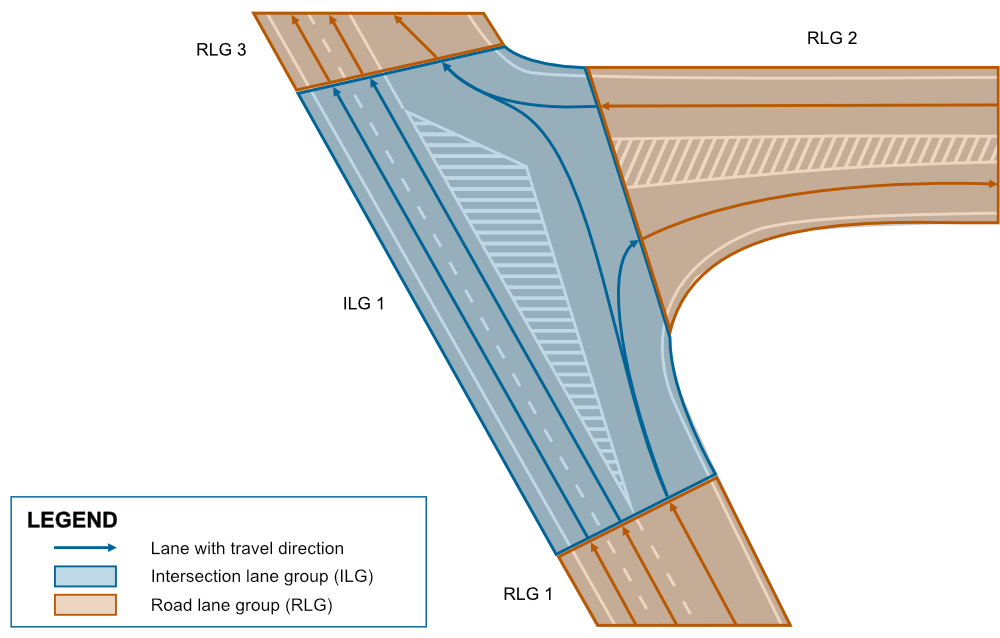
Example with non-functioning road lane groups
In applications that don’t yet support intersection lane groups, we attempt to model this complex intersection using only road lane groups and fork lane groups. However, this approach only works with physical dividers that allow dividing the lane groups. Without these dividers, T-shaped fork lane groups would be necessary, but NDS.Live does not define such structures.
As a result, modeling complex highway intersections without physical dividers can only be achieved using intersection lane groups. Attempting to model this intersection with just road lane groups would look like this:
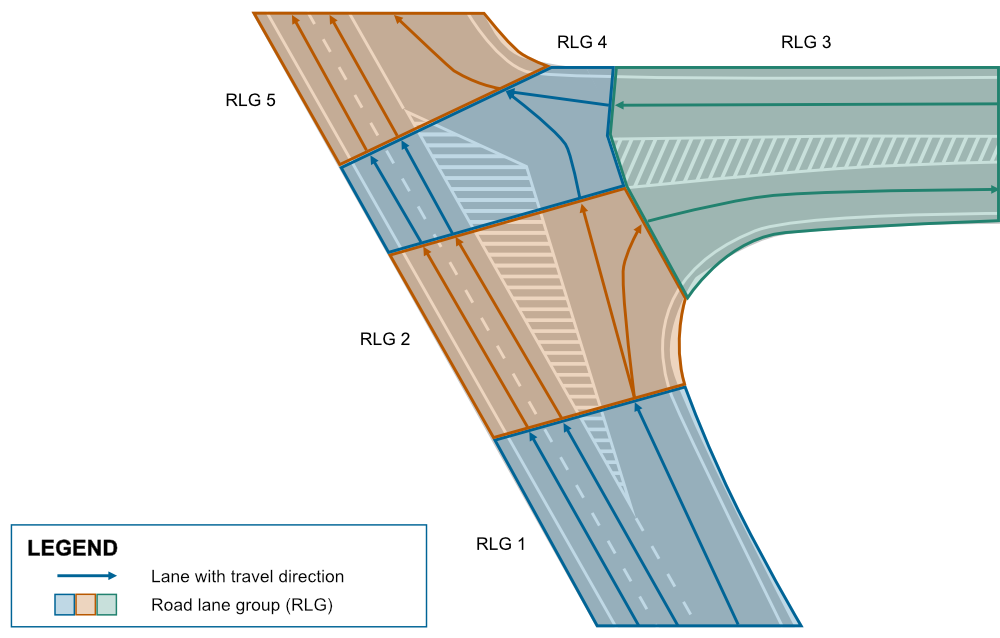
Road lane groups 1 and 2 represent the incoming lanes approaching the intersection from the south. These lane groups are split because a new lane is introduced in road lane group 2.
Road lane group 3 handles both the entry and exit points to the highway from the east, requiring connections to road lane groups 2 and 4.
Road lane group 4 brings in lanes from both road lane groups 2 and 3, while road lane group 5 manages the outgoing lanes from the intersection to the north. A cut is made between road lane groups 4 and 5 due to a change in the number of lanes.
The shaded areas within the intersection are modeled using logical boundaries named GORE. Fork lane groups are used to model connections where a single road lane group branches out into two or more others. In this case, it would create a T-shaped fork lane group, as illustrated in the following figure.
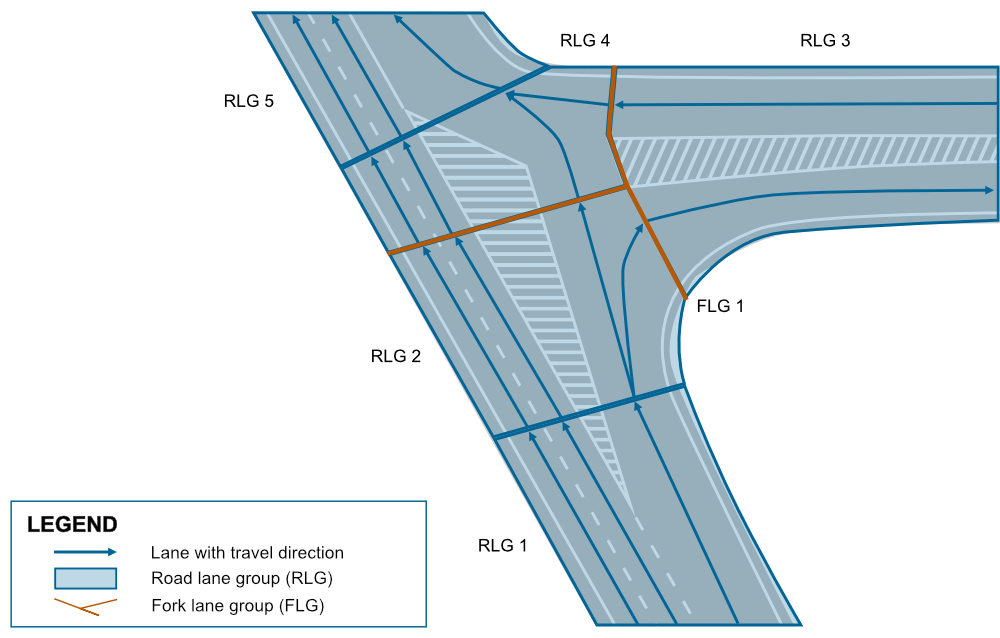
Modeling complex intersections on highways requires careful attention to lane group organization to ensure accurate navigation and safety, especially when physical dividers are absent. NDS.Live utilizes intersection lane groups to maintain proper lane sequencing in these scenarios.
In both the tile border and highway intersection modeling scenarios, NDS.Live Lane Module plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient lane connectivity.

To explore more diverse modeling scenarios and discover how NDS.Live can support your navigation and mapping projects, visit our NDS.Live Developer Portal.
Back to news →